Describe the Process of Dna Replication Using the Following Terms
See the answer See the answer done loading. It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response.
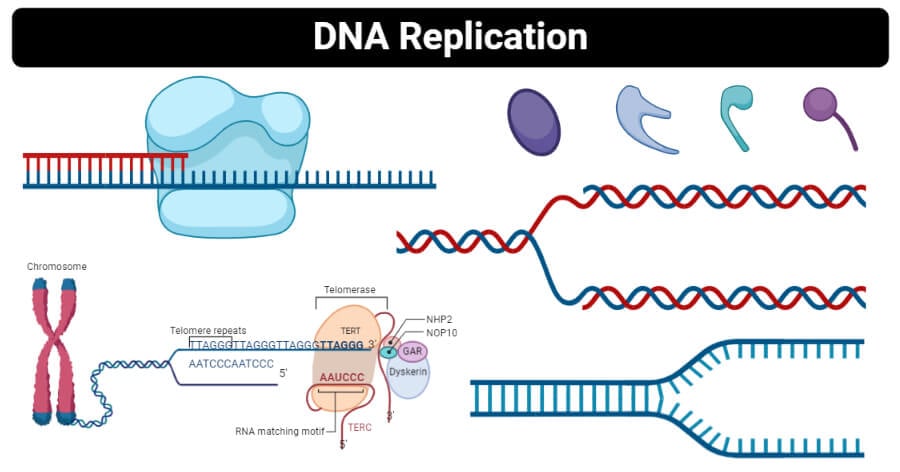
Dna Replication Definition Enzymes Steps Mechanism Diagram
Describe the process of DNA replication including the role of the origins of replication and replication forks.
. The DNA unzips and the enzyme pieces together. Recognition of initiation point DNA replication starts at a specific point called initiation point or origin where replication fork begins. Second now that the bases are.
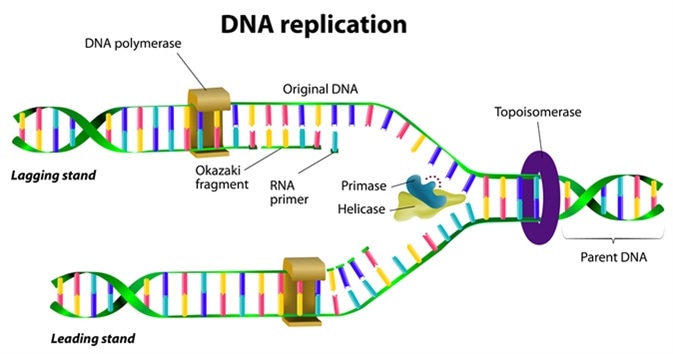
DNA unwinds at the origin of replication. The helix structure is unwound. DNA Ligase The enzyme responsible for sealing together breaks or.
Replication begins at specific sites origins where two parental strands separate to form replication bubbles. This ATP forms the bonds between the base pairs thus breaking the bonds. This exposed the bases that are typically the rungs of the double helix.
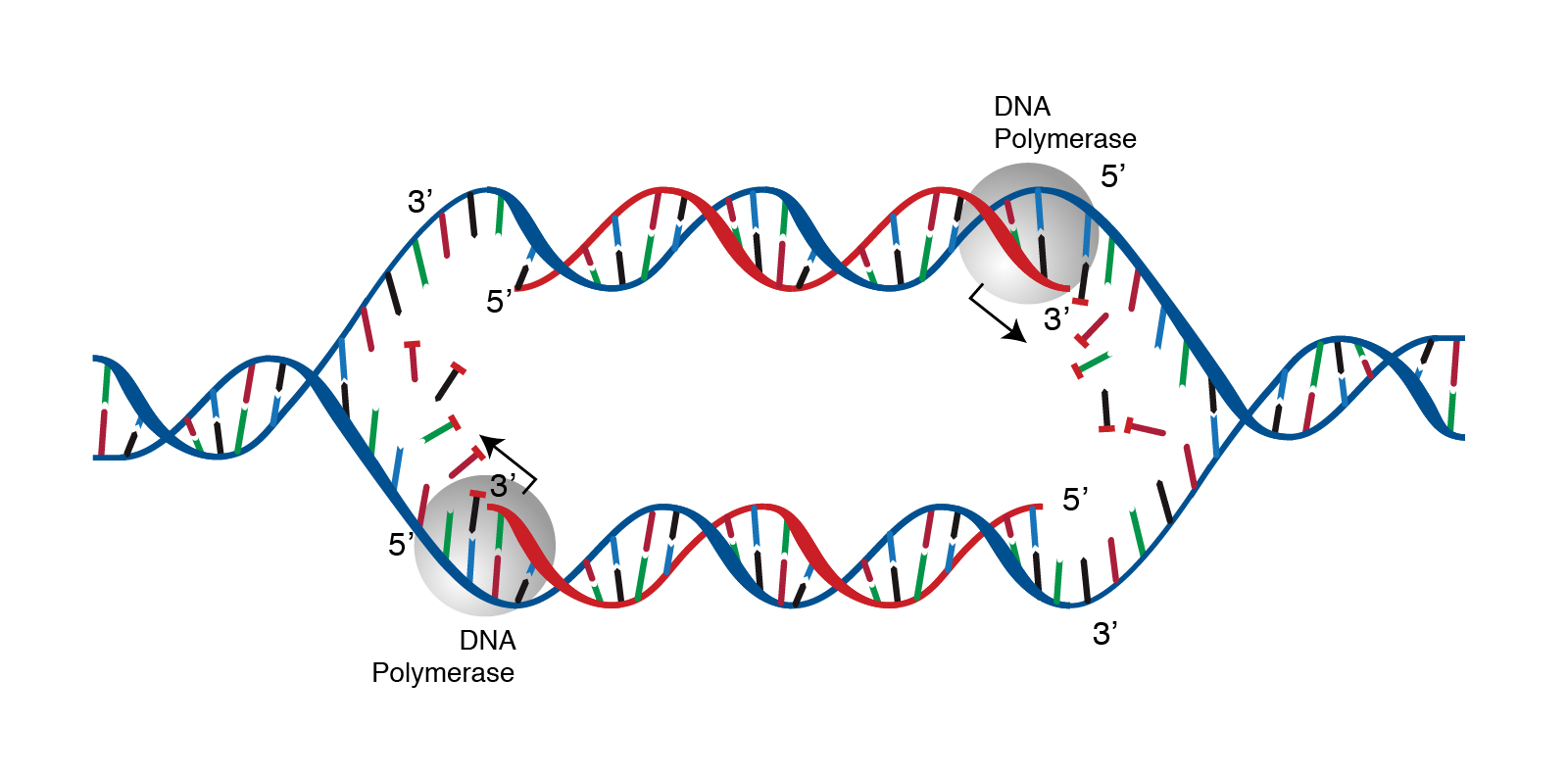
Special molecules break the weak hydrogen bonds between bases which are holding the two strands together. Specific initiation proteins recognize the initiation site on DNA. DNA is directional in both strands signified by a 5 and 3 end.
When a cell divides it must first duplicate its genome so that each daughter cell winds up with a complete set of chromosomes. DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information. DNA polymerase I DNA polymerase III dNTPs DNA helicase single-stranded binding proteins DNA topoisomerase RNA primer primase DNA ligase sliding DNA clamp leading strand lagging strand S phase discontinuous DNA synthesis and continuous DNA synthesis.
Replication follows several steps that involve multiple proteins called replication enzymes and RNA. Synthesizes short RNA sequences known as primers which are required to start DNA replication. DNA replication is the process by which a molecule of DNA is duplicated.
First the double helix is unzipped using DNA helicase. This area will be the template for replication to begin. DNA Polymerase is the main enzyme in the replication process.
In eukaryotic cells such as animal cells and plant cells DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle. During DNA replication a double stranded DNA molecule separate and each strand is used as a template for the synthesis of a new strand. Describe the process of DNA replication including the following terms.
These are extended in both directions. The points where the DNA first are opened are called replication. The process of DNA duplication is called DNA replication.
This is a nucleotide sequence of 100 to 200 pairs of bases. Refers to the newly synthesized strand of DNA that is copied via the addition of complementary nucleotides from one strand of pre-existing DNA during DNA replication. Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding nucleotides 3 to 5.
DNA helicase disrupts the hydrogen bonding between base pairs to separate the strands into a Y shape known as the replication fork. DNA replication Stage one. It is a biological polymerisation which proceeds in the sequence of initiation elongation and termination.
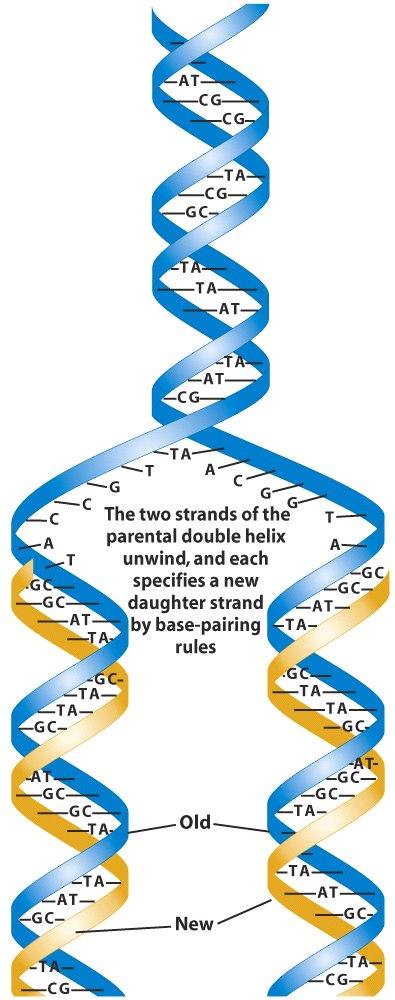
This is called semiconservative replication. 3 DNA ligase and an enzyme that degrades RNA primers to seal together the discontinuously synthesized lagging-strand DNA fragments. DNA replication occurs due to an enzyme.
Describe the role of each of the following enzymes in genomic DNA replication. DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA in which each template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. So each exposed strand acts as a template for replication.
Describe the process by which cells respond to the presence of an A-G pairing of two bases in a newly replicated section of DNA in order to restore the correct base sequence. The complete process of DNA Replication involves the following steps. This is performed by an enzyme known as DNA helicase.
Helicase opens up the DNA-forming replication forks. The process of DNA replication can be summarized as follows. Describe the process of DNA replication.
DNA Helicase The enzyme responsible for separating the two strands of DNA in a helix so that they can be copied during DNA replication. In conclusion DNA replication is the mechanism by which a cell unwinds the DNA double helix and duplicates both. This term captures the idea that each round of DNA replication produces hybrid molecules each of which.
Opens unwinds the double-stranded DNA. Single-strand binding proteins coat the DNA around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of the DNA. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps.
It is an enzyme-catalysed reaction. This results in the formation of two identical copies of the original double stranded molecule. DNA replication is a multistep process where new DNA is made.
The DNA is unwound and unzipped. Define terms related to step 1 Origin of replication Helicase Single strand binding proteins DNA polymerase III Enzyme 3 end Nucleotides Primase Primer Deoxyribonoucleotides Antiparallel Replication fork Leading strand Lagging strand Okazaki fragment DNA polymerase I. Adds new nucleotides to both DNA template strands.
The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing DNA chain. DNA Replication In the process of DNA replication the DNA makes multiple copies of itself. An enzyme DNA helicase unwinds the two strands by hydrolyzing the ATP.
2 DNA helicases and single-strand DNA-binding SSB proteins to help in opening up the DNA helix so that it can be copied. Describe the process of transcription in your own words using the following terms. These include 1 DNA polymerase and DNA primase to catalyze nucleoside triphosphate polymerization.
This is known as the replication fork and here the process of replication begins. Activator enhancer promoter DNA bending protein RNA polymerase transcription factors mRNA transcript.

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication

Dna Replication Worksheet 2015
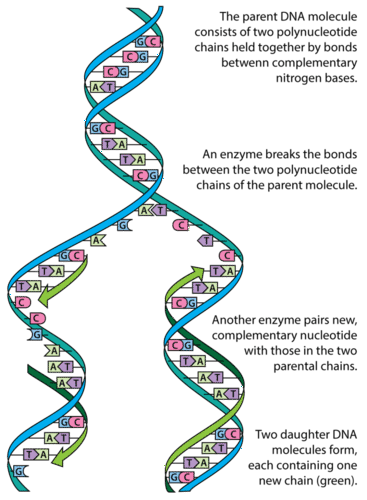
Dna Replication Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
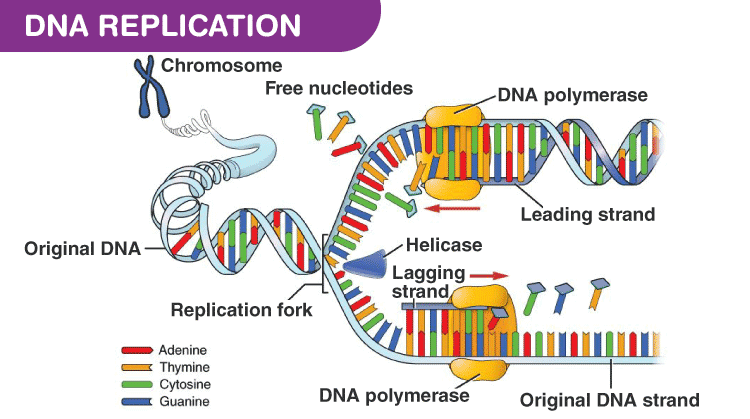
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication

A Explain The Process Of Dna Replication With The Help Of A Schematic Diagram B In Which Phase Of The Cell Cycle Does Replication Occur In Eukaryotes What Would Happen If Cell
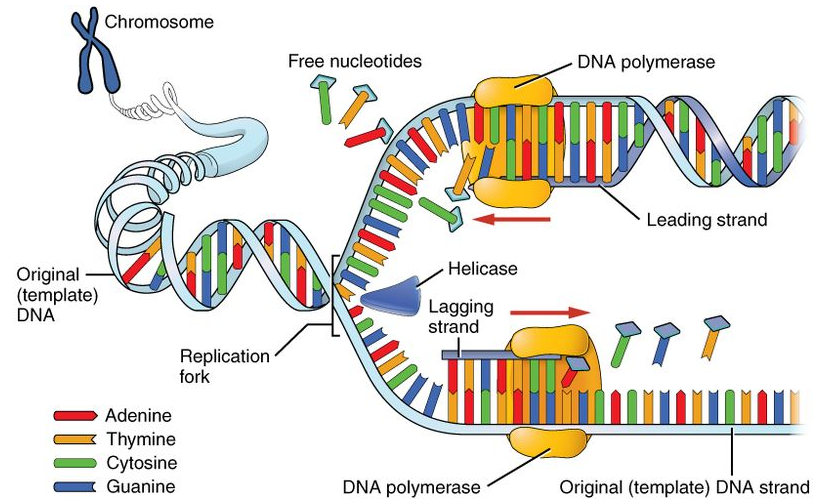
Describe The Process Of Dna Replication With The Help Class 12 Biology Cbse

Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry
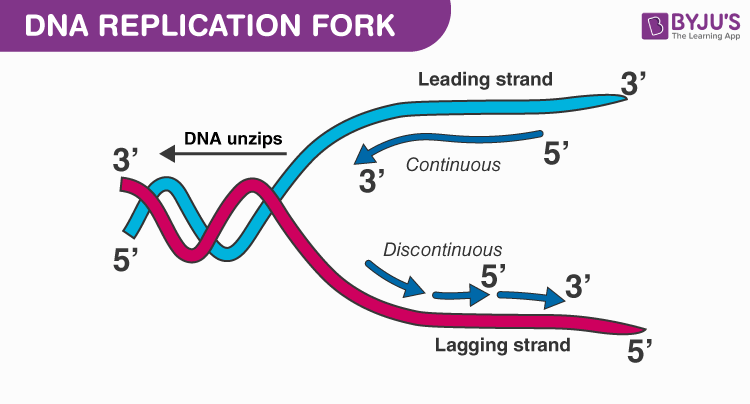
Dna Replication Process With Diagrams Class 12 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Dna Replication

Dna Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
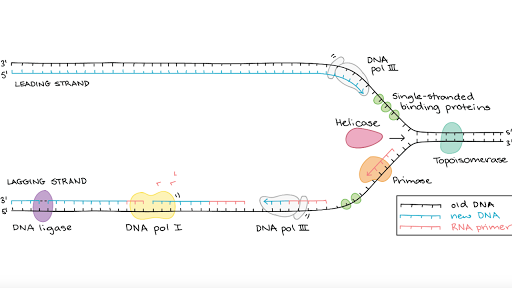
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
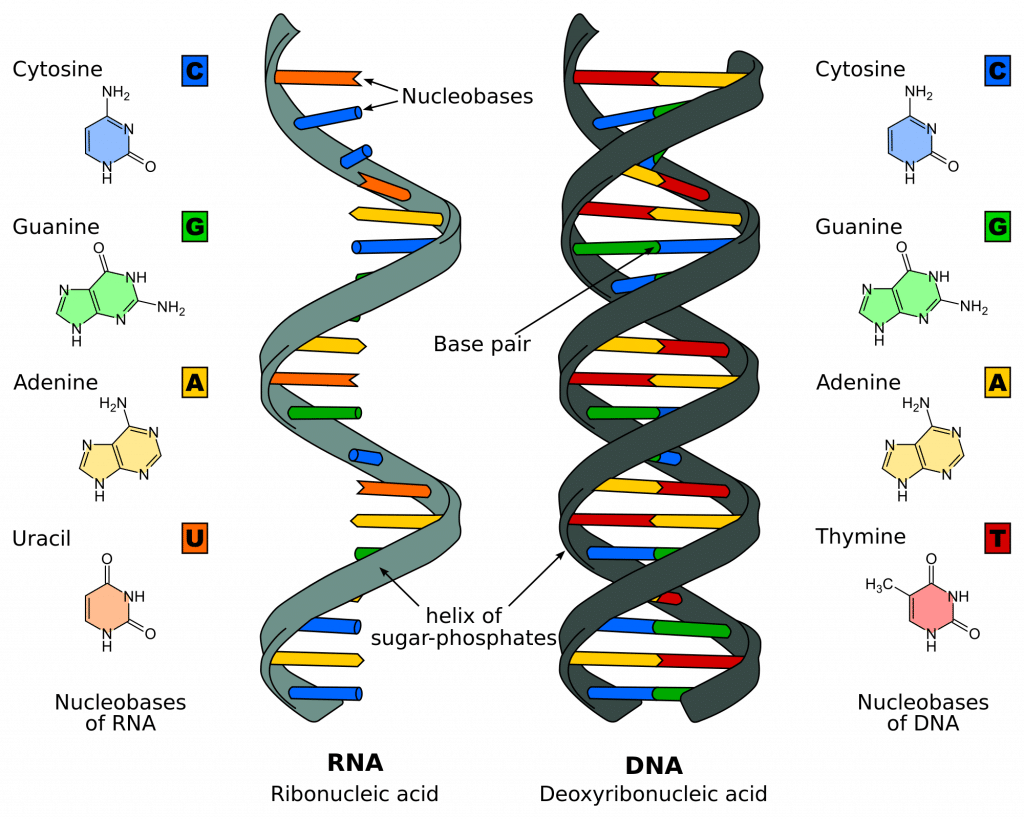
Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
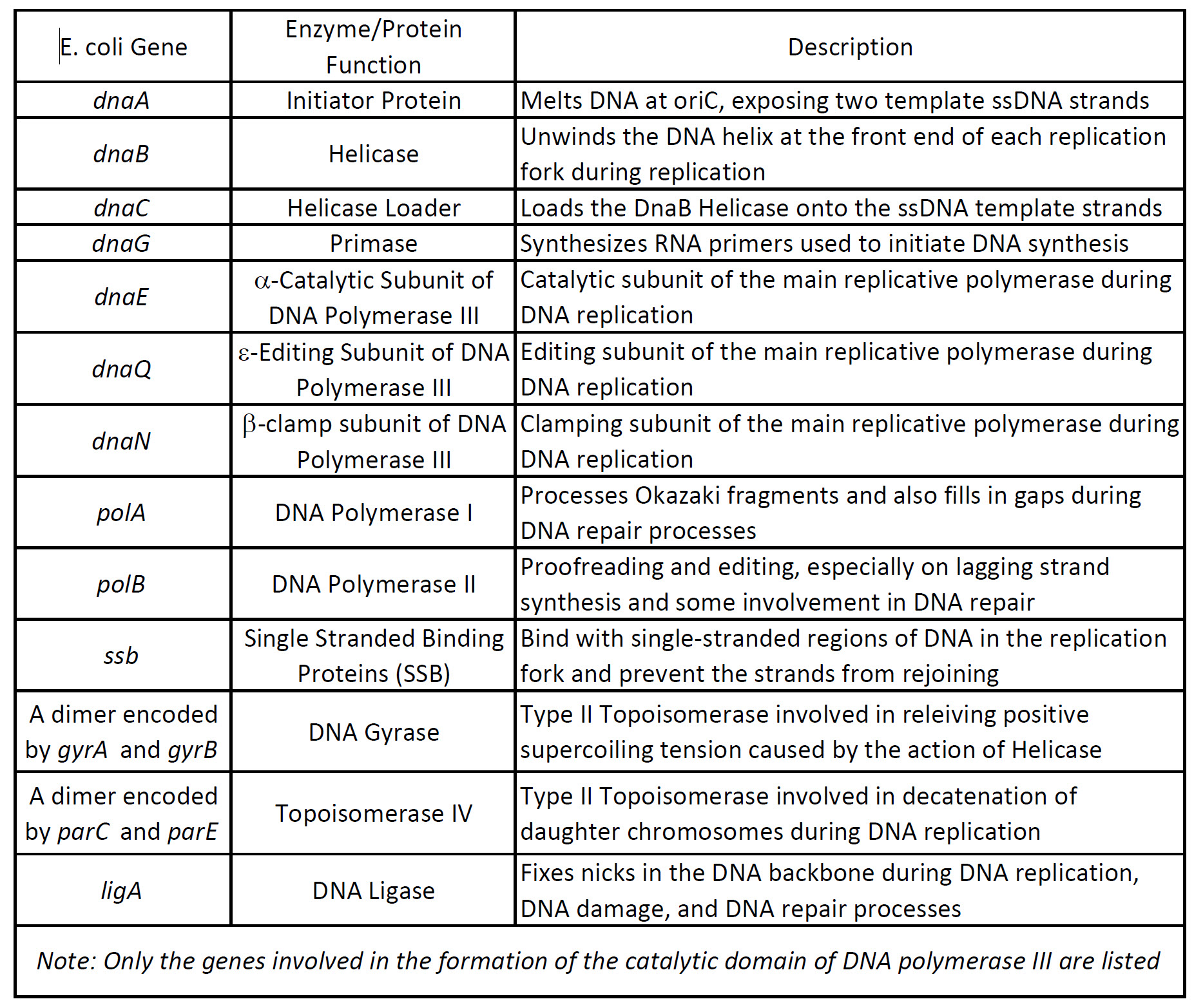
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

Dna Replication S Phase Checkpoint Control Learn Science At Scitable


Comments
Post a Comment